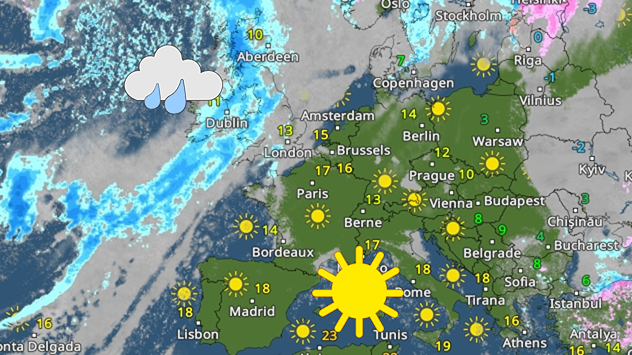
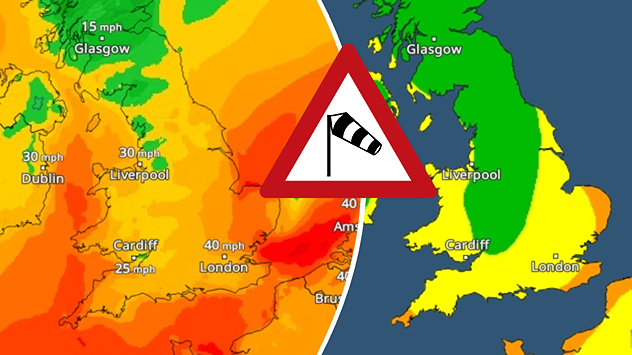
Latest solar activityLarge sunspot visible

Effects of sunspots
Power grids collapse and GPS satellites fail. Mobile phone networks are disrupted for months. Blackouts are possible in conurbations, sometimes with losses running into billions. Radar systems are disrupted and air traffic is affected. Astronauts have to stay in their spaceships because of the strong radiation.